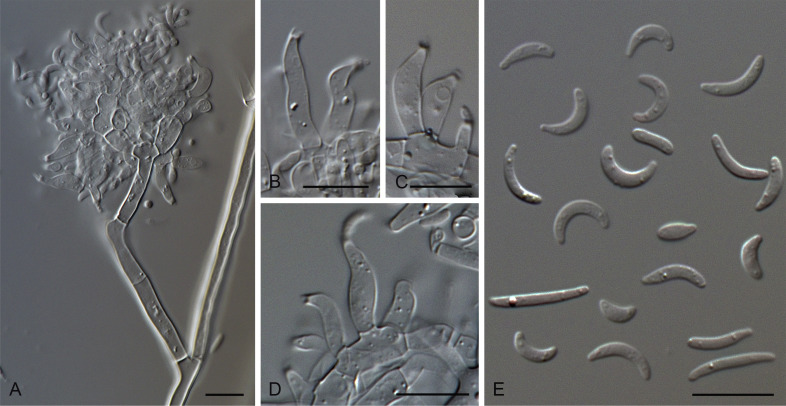
Figure. Gaeumannomyces radicicola (CBS296.53). A. Conidiophores. B–D. Conidiogenous cells. E. Conidia. Scale bars: A–E = 10 μm. Pictures from Hernández-Restrepo et al. (2016).
Gaeumannomyces radicicola (Cain) J. Luo & N. Zhang, in Luo, Walsh & Zhang, Mycologia 107(3): 644 (2015).
MycoBank: MB809635.
≡ Phialophora radicicola var. radicicola Cain, Canad. J. Bot. 30: 340. (1952).
= Harpophora radicicola (Cain) W. Gams, Stud. Mycol. 45: 192. (2000).
= Phialophora zeicola Deacon & D.B. Scott, Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 81: 256. (1983).
≡ Harpophora zeicola (Deacon & D.B. Scott) W. Gams, Stud. Mycol. 45: 192. (2000).
= Gaeumannomyces graminis var. maydis J.M. Yao, Yong C. Wang & Y.G. Zhu, Acta Mycol. Sin. 11: 99. (1992).
Morphological description: Cain (1952), and Deacon and Scott (1983).
Specimen examined: Canada, Ontario, Chatham, isolated from Zea mays, root, 1950, R.F. Cain (isotype of Phialophora radicicola, CBSH-7592, CBSH-7593; culture ex-isotype of Phialophora radicicola, CBS296.53). South Africa, unknown locality, isolated from Zea mays, Feb. 1984 (isotype of Phialophora zeicola, CBSH-7597; culture ex-isotype of Phialophora zeicola, CBS149.85). (Hernández-Restrepo et al. 2016).
Hosts/substrates: From Zea mays.
References:
Cain RF. 1952. Studies of fungi imperfecti I. Phialophora. Canadian Journal of Botany 30:338–343.
Deacon JW. 1974. Further studies on Phialophora radicicola and Gaeumannomyces graminis on roots and stem bases of grasses and cereals. Transactions of the British Mycological Society 63:307–327.
Hernández-Restrepo M, Groenewald JZ, Elliott ML, Canning G, McMillan VE, Crous PW. 2016. Take-all or nothing. Studies in Mycology 83:19–48.
Geographical distribution: Canada, Ontario, Chatham. China, Liaoning. South Africa.
Copyright 2022 by The American Phytopathological Society. Reproduced, by permission, from Luo, J., and Zhang, N. 2022. The Rice Blast Fungus and Allied Species: A Monograph of the Fungal Order Magnaporthales (https://my.apsnet.org/APSStore/Product-Detail.aspx?WebsiteKey=2661527A-8D44-496C-A730-8CFEB6239BE7&iProductCode=46826). American Phytopathological Society, St. Paul, MN.