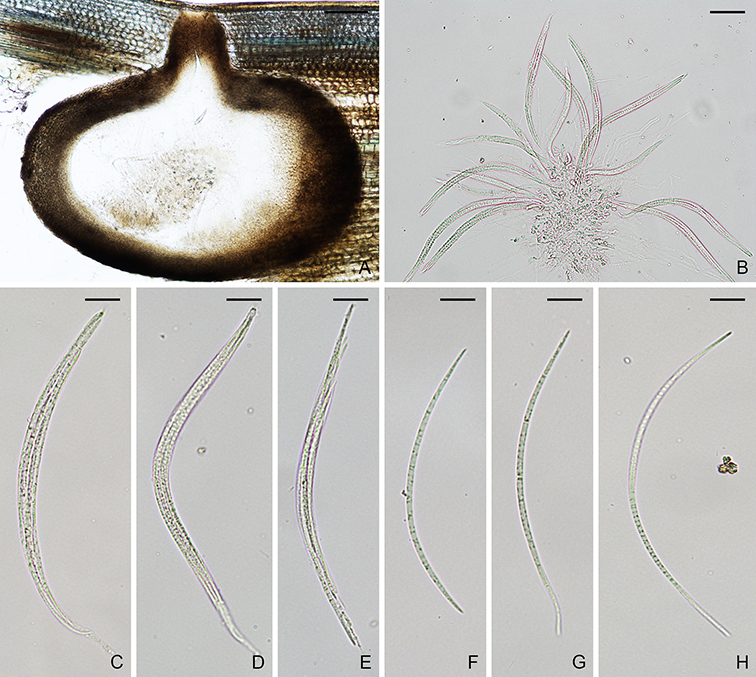
Figure. Kohlmeyeriopsis medullaris (NYBG1315597). A. Ascomatum. B–E. Asci. F–H. Ascospores. Scale bars: A = 100 µm; B = 40 µm; C–H = 20 µm.
Kohlmeyeriopsis medullaris (Kohlm., Volkm.-Kohlm. & O.E. Erikss.) Klaubauf, M.-H. Lebrun & Crous, Stud. Mycol. 79: 101 (2014).
MycoBank: MB810198.
≡ Gaeumannomyces medullaris Kohlm., Volkm.-Kohlm. & O.E. Erikss., Mycologia 87(4): 540 (1995).
= Trichocladium medullare (asexual state) Kohlm. & Volkm.-Kohlm., Mycotaxon 53: 349 (1995).
Ascomata perithecial, immersed, solitary, globose to subglobose, dark brown to black, 550–750 µm diam, with a dark brown to black, cylindrical neck, 150–250 × 120–150 µm. Paraphyses hyaline, septate. Asci 8-spored, unitunicate, cylindrical, 130–175 × 7–9 µm, with a refractive ring. Ascospores parallel in ascus, filiform, curved, 3–7-septate, not constricted at septum, hyaline to yellowish, smooth, 95–165 × 2.5–4 µm. Asexual state trichocladium-like. Hyphae branched, septate, hyaline to light brown, smooth. Conidiophores short, branched. Conidia two-celled, smooth; apical cell ellipsoidal, aseptate, dark brown, 13.5–20.5 × 7–10 µm; basal cell cylindrical or obconical, 0(–1) septate, light brown, 3.5–6 × 3–5 µm (Asexual state description from Kohlmeyer and Volkmann-Kohlmeyer, 1995).
Typification: Holotype IMSJK5528. Isotype NY1315597. Paratype, NY1315595. Ex-holotype culture CBS117849.
Specimens examined: USA, North Carolina, Carteret County, Broad Creek, on dead standing culms of Juncus roemerianus, 16 Mar. 1994, J. Kohlmeyer, 5528 (NY1315597, CBS117849); ibid., 28 Nov. 1993, J. Kohlmeyer, 5522 (NY1315595).
Gene sequences: KM484852 (ITS), KM484968 (28S), KM485068 (RPB1).
Hosts/substrates: On dead culms of Juncus roemerianus (Juncaceae).
Distribution: USA (North Carolina).
Copyright 2022 by The American Phytopathological Society. Reproduced, by permission, from Luo, J., and Zhang, N. 2022. The Rice Blast Fungus and Allied Species: A Monograph of the Fungal Order Magnaporthales (https://my.apsnet.org/APSStore/Product-Detail.aspx?WebsiteKey=2661527A-8D44-496C-A730-8CFEB6239BE7&iProductCode=46826). American Phytopathological Society, St. Paul, MN.